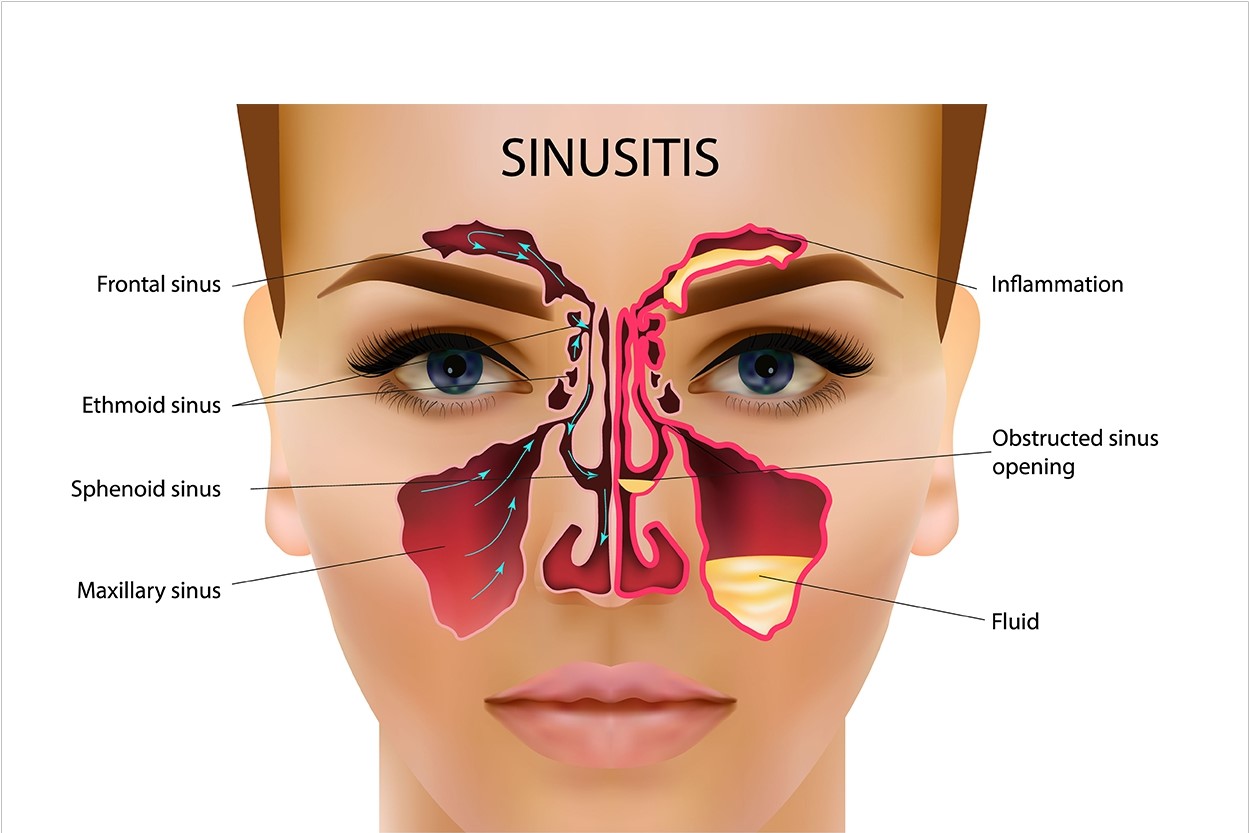
Sinusitis is an inflammation, or swelling, of the tissue lining the sinuses. The sinuses are four paired cavities (spaces) in the head. They are connected by narrow channels. The sinuses make thin mucus that drains out of the channels of the nose. This drainage helps keep the nose clean and free of bacteria. Normally filled with air, the sinuses can get blocked and filled with fluid. When that happens, bacteria can grow and cause an infection (bacterial sinusitis).
Sinusitis usually happens after you've had a cold or allergies. But certain symptoms will keep going, even after your cold goes away. You'll probably have a stuffy nose and cough for more than a week or two. You may hear your doctor talk about two kinds of sinusitis: "acute" and "chronic." There's a simple way to tell them apart. If your symptoms last less than 4 weeks, it's acute. If they go on for 3 months or longer, you have chronic sinusitis.
This is also called rhinosinusitis, with “rhino” meaning “nose.” The nasal tissue is almost always swollen if sinus tissue is inflamed.
The symptoms of allergies and sinusitis overlap a lot. Both can give you a stuffy nose. If it's allergies, you may also have:
• Runny nose and sneezing